Types of Air Conditioners: Understanding How They Work

Understanding the Different Types of Air Conditioners and How They Work
There are several different types of HVAC systems, and while they all have the ability to keep your home nice and comfy no matter what the outside temperature may be, each one achieves that goal in a different way. Understanding the differences helps you decide which type is best suited for your climate, home type, personal preference, and other needs.
Let's look at each one and see how they differ.
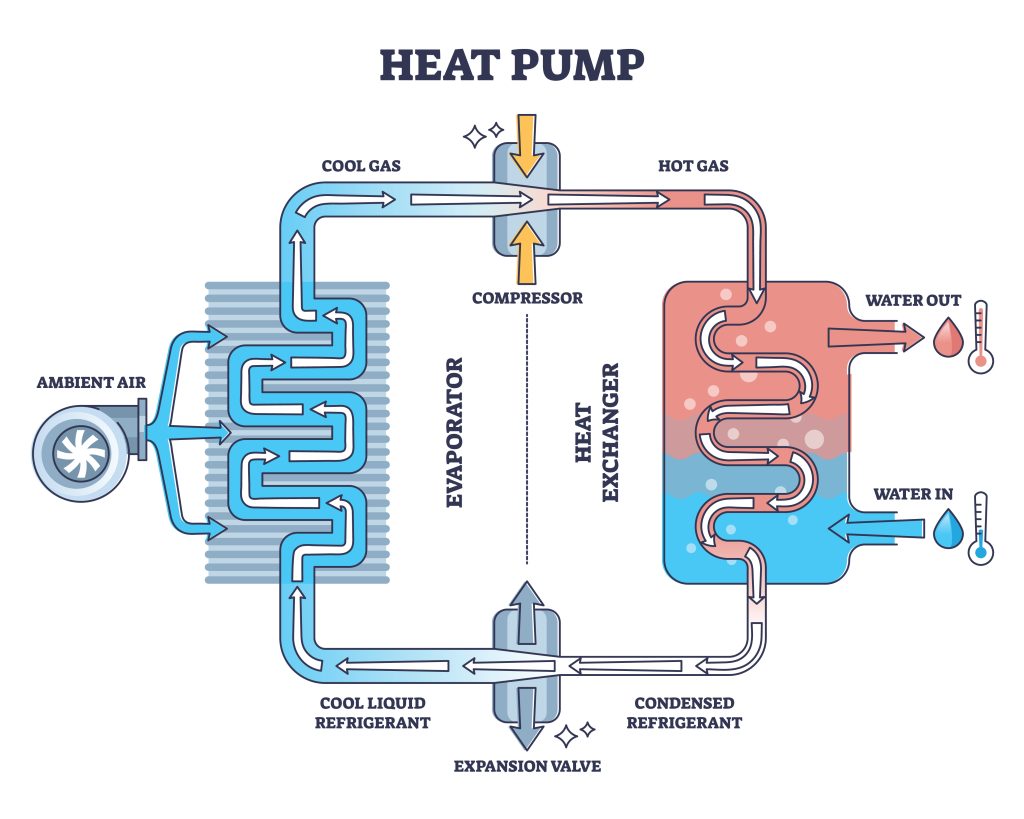
Heat Pump System
Among the different types of air conditioners, when you are looking for the most efficient HVAC system, a heat pump is often the answer. Utilizing a reversible refrigeration cycle that transfers heat between the indoor and outdoor environments via a special valve, heat pumps use the least amount of energy to heat and cool your home. This reversible refrigeration action allows it to provide both heating and cooling functions from the same system.
Cooling Mode
When in cooling mode, the heat pump operates very similar to a traditional air conditioner. The systems coolant, such as R22 or 410A, absorbs heat from the indoor air and releases it outside. This extraction of heat from your indoor living space leaves your indoor air cooler. There is no transfer of air from inside to outside, only temperature, or more specifically heat. Your air conditioner does not bring in fresh air from outside, or remove air from inside.
Heat Mode
In heat modem your heat pump extracts heat from the outside air and transfers it indoors. Even if it is fifty degrees outside, that outside air temperature is warmer than the temperature of your system's coolant, and so the colder coolant can warm itself with the outside air, bring that heat inside, and release it into your home.
There is, however, a downside to the heating side of heat pumps. This system only works to heat your home if the outside air temperature stays above the temperature of your coolant. At below 40° outside air temp the heat pump starts losing efficiency, and at 25° outside air temp it becomes less efficient than a gas furnace. These limitations cause it to not be as popular in colder climates.

Straight Cool System with Electric Heat Strips
Straight cool units are usually found in warmer climates where heating is not as much of a concern. It utilizes the same refrigeration cycle as a heat pump to cool your home, but it does not come equipped with the ability to reverse its process of cooling to heating like a heat pump.
Inefficient Heating
Instead, these systems are usually installed with an electric heat strip kit that can be used to provide heat. These electric heat strips are activated as electricity flows through them and causes the coils to generate heat the heat is then transferred to the air passing over the strips within the air handler. Think of this like a sized-up version of an electric floor heater with coils that get red hot and heat the air as it passes over them. While electric strips will provide adequate heating, this is the most cost inefficient way to warm your home.
Size Matters
Another reason these units are often selected is their size. Having no furnace and not being as bulky as a heat pump, straight cool systems with electric heat strips are found in a lot of condos and apartments where space is limited. These are not as small as ductless mini-split air conditioners, nor as energy efficient, but they are typically the smallest central air conditioner type that you can find.

Straight Cool System with Gas or Propane Furnace
Furnaces are most often found in colder climates where a heat pump system would not function properly. Compared to a heat pump, a furnace is considered a more effective (though less energy efficient) means of heating, thus adding to its value in colder climates.
Cools Like Any Other Unit, Heats Like a Champ
The cooling portion of a furnace functions the same as a straight cool or heat pump, with the difference being the heating is provided by a gas or propane furnace in lieu of a heat pump or electric strips. A gas or propane furnace warms the air in your home by utilizing a heat exchanger, which is a metal chamber with a series of coils and tubes that absorb heat from the burning gas. While more efficient than electric heat strips, gas furnaces aren't a favorite for their efficiency, but instead for their ability to rapidly heat any living space. The air they blow also feels warm, blasting out air that is dozens of degrees warmer than the air in your home. Heat pumps are often criticized for their warm air not feeling hot despite their ability to warm your home. This is because heat pumps blow out air only a few degrees warmer than the air in your home providing efficient, gradual heating compared to a gas furnace that bombards you with heat on demand.
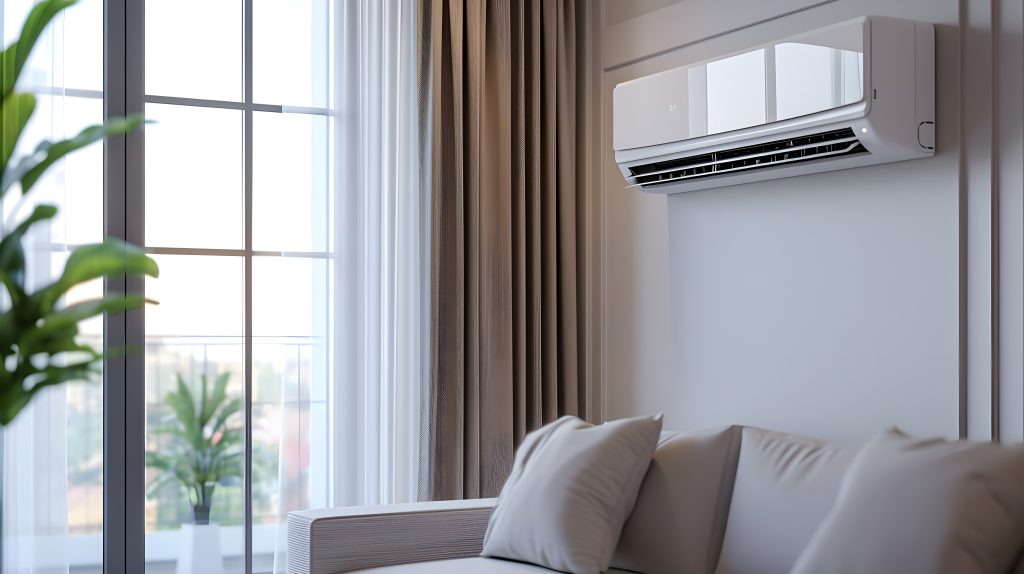

Ductless systems
Mini Split
Other types of air conditioners include the ductless systems. Mini-split units are the most common. They are a type of HVAC system that can provide both heating and cooling to individual rooms or within certain zones of your home. Unlike a traditional AC system, it does not utilize duct work to move the air around your home. Instead it blows cooled or heated air straight from the wall-mounted interior unit.
Mini-split systems consist of two major parts: the interior air handling unit and the outdoor condenser/compressor unit. The interior portion is mounted on the wall in the room where you are providing heating and cooling. The outside unit is placed on the ground or affixed to the exterior wall.
These types of systems offer several advantages as they don't require a duct system. As a disadvantage, however, they are limited by their inability to heat or cool a large space or multiple rooms without using multiple units.
Standalone Furnace
A standalone gas or propane furnace is a great choice for a project that doesn't require cooling. When choosing between electric, propane, or gas, it is the natural gas furnace that is the most efficient standalone form of heating. It works by igniting the gases and passing them through a heat exchanger that is made-up of metal tubes and coils. The exchanger captures the heat from the gases without allowing them to be mixed with the clean air from your home.
These units can be tied in to an existing duct systems to provide heat to a large area or mounted to the wall to provide heat to a specific area.
Standalone Electric Heater
These are generally a terrible idea. As one evaluator once quipped, 'it would be more efficient to set $100 bills on fire to stay warm than to use a standalone electric heater.' While burning money may be a bit dramatic, it's not too far off from what this type of unit usually does to your power bill. The mini-split heat pump or gas or propane furnace will prove much more energy efficient and economical.

Other Types of Air Conditioners
While there are other types of central heating and cooling systems, like portable air conditioners, chiller systems, and geothermal, these other types are much less common and/or practical. Geothermal, chillers, and other nonstandard units are nonstandard for a reason. They're usually cost prohibitive and only make sense in specific circumstances. Additionally, they're availability is limited. Very few local companies can work on nonstandard A/C types and parts and equipment are rarely available locally.
Do You Have Questions About the Types of Air Conditioners?
We're happy to help with assessing what system type may be best suited for your living or work space. If you'd like a free assessment and estimate, just give us a call.
- Free Estimates - No-hassle estimates!
- Free Assessments - Schedule now!